Cereals are the edible seeds or grains of the grass family, Gramineae. A number of cereals are grown in different countries, including rye, oats, barley, maize, triticale, millet and sorghum.
Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.), originally from the Middle East, was one of the first plants domesticated for human consumption and was known for its vast geographical distribution. Barley has many uses, for instance it can be served as animal fodder, as base malt for beer and certain distilled beverages, and as a component of various health foods. It is used in soups and stews, and in barley bread of various cultures.
Pearled barley is eaten in soups and stews in the UK and in the Far and Middle East; barley is also used in bread (as flour) and ground as porridge in some countries.
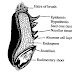
The major parts of the barley grain are the endosperm, the embryo and their covering layers of maternal origin. The endosperm consists of the starchy endosperm and a surrounding aleurone layer (Figure 2). The starchy endosperm forms the largest morphological part of the barley grain comprising c. 75% of its weight. The function of the starchy endosperm is to serve as a nutrient storage for the growing embryo during germination.
Barley is characterized by a thick fibrous coat, a high level of ß-glucans and simply-arranged starch granules. World production of barley is about 30 % of that of corn. In comparison with corn, barley has more protein, methionine, lysine, cysteine and tryptophan.
Barley grain is an excellent source of soluble and insoluble dietary fiber (DF) and other bioactive constituents, such as vitamin E (including toco-tri-enols), B-complex vitamins, minerals and phenolic compounds.
Barley is also a rich source of tocols, including tocophenols and toco-tri-enols. Barley contains3-11% dietary fibers made up of pentosans, beta-glucan and cellulose. Barley has an attractive nutrient make-up which makes it an excellent food for health-conscious people.
Barley a minor cereal
Antioxidant and Health Benefits of Cantaloupe Juice
-
Cantaloupe juice is a rich source of antioxidants, particularly vitamin C
and flavonoids, which help protect the body from oxidative stress and
inflammatio...