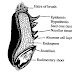
The rice plant is a member of Poaceae (old Gramineae) family. The common cultivated rice plant is an annual which usually grows to a height of a half meter or two meters but there are certain varieties that grow much taller (6-9 metres).
Most cultivated rice is grown in flooded fields and rain fed lowlands. Irrigated rice is defined as rice produced when water is added to supplement that supplied by natural processes such as rainfall.
Planting within the recommended sowing window allows fast, uniform crop that will have higher yields, the highest probability of limited cold stress at microspore, and high grain quality at harvest.
It also will help produce a fast-growing, and will be better able to compete with weeds and pests. The best time to plant depends on the locality, variety, water availability, and the best harvest time. Rice can either be transplanted from a nursery or direct-seeded in the field.
Transplanted crops will normally take less time in the production field but 10–15 days longer for the total crop duration. In both cases, a well-prepared seedbed is needed.
Most soils provide only limited amount of nutrients to the crop, therefore fertilizers need to be applied to increase grain yield. In some cases, fertilizers are also added to improve the soil’s physical condition.
Rice is ready for harvesting at about 80% grain maturity, when the grain color turns to golden yellow.
Rice plant cultivation
Antioxidant and Health Benefits of Cantaloupe Juice
-
Cantaloupe juice is a rich source of antioxidants, particularly vitamin C
and flavonoids, which help protect the body from oxidative stress and
inflammatio...