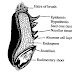
Wheat produces a white flour. In addition, the unique properties of wheat protein alone can produce bread dough of the strength and elasticity required to produce low density bread and pastries of desirable texture and flavor.
All wheat belong to the genus Triticum of the family Gramineae. The majority of the wheat grown in the world for food belongs to two major species, Triticum aestivum and Triticum durum.
Wheat generally is classified by its physical characteristics such as kernel color, harvest season and protein content.
There are many varieties of wheat. They may be classified as:
• Hard red winter wheat
• Hard red spring wheat
• Soft red winter wheat
• Hard white wheat
• Soft white wheat
• Durum wheat
• Mixed wheat
Hard wheat is the term applied to varieties that are high in protein (10-18%). Hard wheat berry is actually quite difficult to break. Soft wheat is the term applied to varieties that are lower in protein (8-11%).
Hard wheat produce more elastic dough than soft wheat. Therefore, hard wheat are used for breads, and soft wheat are used for cakes.
Durum wheat are most used for alimentary pastes (spaghetti, macaroni, etc.) and for the thickening of canned soups.
Winter wheat are planted in the fall and harvested in the late spring or early summer. Spring wheat are planted in the spring and harvested late summer.
The term red wheat and white wheat are used to describe the appearance of the grain’s bran and color of flour made from the whole grain. Red wheat is more common but white wheat has grown significantly in the last decade.
Mixed wheat is any mixture of what that consist of less than 90% of one class and more than 10% of one other class or a combination of classes that meet the definition of wheat.
Wheat classifications