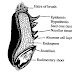
Oats and their products have been known for many years to possess antioxidants properties. The epicatechin concentration is highest in the hull fraction supporting the link between phenolics and antioxidant activity.
Oats posses antioxidant capacity most of which is likely derived from polar phenolic compounds in the aleurone.
Phenolic compounds and tocols are mainly regarded as being responsible for oat antioxidant activity. Oat sterols have also been reported to have antioxidant properties. Study in 2001 found that the cultivar had significant impact on the antioxidant activity of oats. The antioxidant activity differences were likely due to the significant differences in phenolic composition of the cultivars.
The polyphenols of oats have also recently been found to exhibit anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative and anti-itching activity, which may provide additional protection against coronary heart disease, colon cancer and skin irritation.
Oats contain unique antioxidant polyphenols called avenanthramides not found in other cereals.
These metabolites are a unique group of antioxidants found almost exclusively in oats.
Oats antioxidant
Antioxidant and Health Benefits of Cantaloupe Juice
-
Cantaloupe juice is a rich source of antioxidants, particularly vitamin C
and flavonoids, which help protect the body from oxidative stress and
inflammatio...