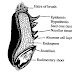
Dietary fiber is defined as the components of plant cells that resist digestion by human digestion enzymes.
Dietary fiber includes the non-digestible carbohydrates. It is classified as either soluble or insoluble. Both have nutritional significance.
The water insoluble group that includes wheat products and wheat bran is to improve intestinal health and is thought to reduce the risks of certain cancers.
The water-soluble fibers such as those found in the brans of some cereals (e.g., oats and rice) and in pectin are believed to lower the levels of serum cholesterol by binding with bile acids and causing removal of cholesterol in the feces.
The major component of natural dietary fiber are cellulose, hemicelluloses, lignin and other non-starch plant polysaccharides such as pectin.
Whole wheat grains are good sources of dietary fiber. Bran is high in dietary fiber. In fact, the bran is about 42 percent of dietary fiber, most of it classified as insoluble fiber.
The consumptions of fiber is recommended, although not to excess. It appears that excessive amounts of dietary fiber may interfere with the retention of minerals required by the body.
Dietary fiber in grain
Antioxidant and Health Benefits of Cantaloupe Juice
-
Cantaloupe juice is a rich source of antioxidants, particularly vitamin C
and flavonoids, which help protect the body from oxidative stress and
inflammatio...