Cereal is any member of the grass family (Gramineae) which produced edible grains usable as food by humans and livestock.
Cereals provide more food for human consumption than any other crops. All cereal grains have fairly similar structure and nutritive value, although the shape and size of the seed may be different.
Common cereals are rice, wheat, barley, oats, maize (corn), sorghum, rye, and certain millets, with corn, rice, and wheat being the most important.
Cereal grains supply most of their food energy as starch. Cereal and grain legumes together may contribute 70% to 90% of the calories in the daily diet and a almost similar of of dietary protein.
They are also a significant source of protein, though the amino acid balance is not optimal. Whole grains are good sources of dietary fiber, essential fatty acids, and other important nutrients.
Rice is the most important of the cereals used as the staple food by more than half of the world’s population.
Rice is eaten as cooked entire grains, although rice flour is also produced. Oats are rolled, ground, or cut into bits (steel-cut oats) and cooked into porridge. Most other cereals are ground into flour or meal, that is milled.
The whole grain of all cereals have a nearly similar composition. On an average, the important cereals contain about 1 g% protein, 1 g% fat, and about 70 g% carbohydrate and yield about 340 kcal energy per 100g.
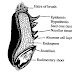
Bran, which represents 7% of the grain, contain the majority of the grain fiber, essentially cellulose and pentosans. It is a source of B vitamins and phytochemical and 40-70% of the minerals are concentrated in the outer layer.
The endosperm, the main part of the grain (80-85%), contains mostly starch.
Health-conscious people tend to prefer whole grains, which are not milled. Overconsumption of milled cereals is sometimes blamed for obesity. Milled grains do keep better because the outer layers of the grains are rich in rancidity-prone fats.
Chemical composition and nutritive value of cereal grains are affected by variety and location of production.
Nutritive Value of Cereal
Antioxidant and Health Benefits of Cantaloupe Juice
-
Cantaloupe juice is a rich source of antioxidants, particularly vitamin C
and flavonoids, which help protect the body from oxidative stress and
inflammatio...