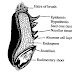
In celiac disease, the antibodies that attack the intestine have their most obvious effect in the villi, which become stunted and almost flat.
People who have celiac disease cannot tolerate protein called gluten which is found in wheat, rye and barley. In addition to sensitivity to gluten, the early introduction of cow’s milk is believed to be a major causative factor of celiac disease.
Celiac disease is a lifelong disorder than can present at any age. Approximately 1 in 200 people in North America are affected, however, may cases of celiac disease are undiagnosed.
Celiac disease causes weight loss, diarrhoea, abdominal pain, anaemia, bloating, distension and bulky and fatty stools. They may also be bone softening from mineral and vitamin deficiency.
These symptoms are due to food retention in the intestine and nutritional losses from failure of absorption.
Celiac disease affects people differently. Some people develop symptoms as children, others as adults, One factor thought to play a role in when and how celiac disease appears is whether and how long person was breast-fed – the longer one was appear and the more atypical the symptoms.
What is celiac disease?